See also: Band Spotter, DX Spot Manager
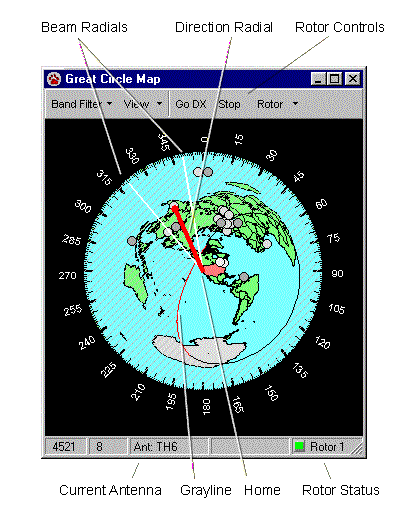
The CommCat Great Circle Map provides a view of the world making it easy to determine the bearing and distance to any point. The map is centered on your location as determined by the longitude and latitude you enter in the File, Settings, Station window.
Land areas are shown on the map in green (except for Antarctica which is gray), while water is blue. Your country is shown in red. A bearing key encircles the map, and as you move the mouse pointer, the bearing and distance from your home to the mouse pointer are shown in the status bar at the bottom of the window.
DX Spots
The most recent DX spots are superimposed on the map. The number of spots, and the color and shape (square or round) of spots are determined by rules you establish in the DX Spot Manager. As you move the mouse pointer over a spot, the call sign and frequency of the spot are shown as a tool tip. Double-click any spot to tune your rig to the frequency for that spot.
Change the maximum number of spots included on the map using the File, Settings, Spots window. If a spot is not shown on the map due to this number, double-clicking a spot in the DX Spot Manager may not result in a correct beam heading.
The most recent spots listed in the DX Spot Manager show in the map. In the map View menu, select All Spots to show all spots, or Selected Folder to show the spots in a selected folder in the DX Spot Manager.
Resizing the Map Window
To resize the map window, drag the lower right corner of the window to the size you wish the window to be. Redraw the map in the resized window by clicking Resize on the View menu.
Other View Options
The Circle Map View menu has options for controlling the information provided on the map. Items such as the gray line, spots, and beacon markers can be turned on and off from this menu.
Moving the Great Circle Map Out of the CommCat Main Window
If you wish to move the Great Circle Map window out of the Main CommCat window, check the Circle Map option on the File, Settings, Program, Window Position window. This option is useful if you want to display the Great Circle Map while using another program, or you have a dual monitor system.
Band Filter
Choose Band Filter Settings from the Band Filter menu to open the Band Filter window.
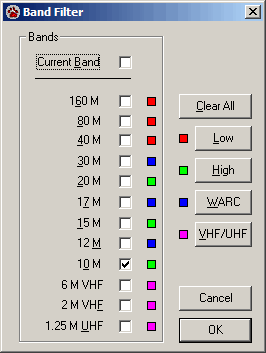
Use the Band Filter to reduce the number of spots displayed. You can include spots from the current band, a selected band, or a selection of bands. The Band Filter does not use the Rule system. Even though you do not see the spots on the Great Circle Map that are hidden by the Band Filter, they remain in the DX Spot Manager Rule processing list. To engage the Band Filter, click the Band Filter button on the Great Circle Map toolbar.
Two types of Band Filtering are provided. To make a selection, click the Down Arrow to the right of the Band Filter button and then Band Filter Settings. You can limit the spots to the "Current Band" or to a combination of specified bands.
The Current Band option hides all spots in the spot list except those on the same band as your radio. As you tune from one band to another, the filtering tracks the current band.
You can also specify a band or set of bands you wish to monitor. When a band is selected a check mark appears next to the band name. Click a band name to add or remove a check mark. If a band has a check mark, spots on that band are not displayed.
The Band Filter settings in the Great Circle Map window also apply for the DX Spot Manager.
Antenna Rotor control
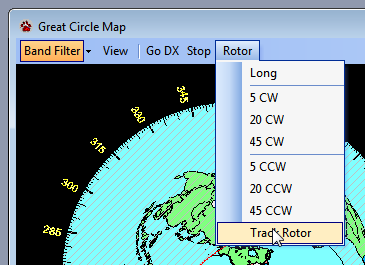
The Great Circle Map provides commands to antenna rotor controllers. The current direction of the antenna is shown by the two radial yellow lines. Buttons on the Map toolbar are used to control the rotor. You can turn rotor tracking on and off by using the Track Rotor option in the Rotor menu.
To rotate your antenna to a DX station's bearing, double-click any DX spot, then click Go DX on the Great Circle Map toolbar (or press F11). When you double-click a spot, your radio is tuned to the spot frequency. You can also double-click any point on the map not associated with a spot to set a bearing. Finally, you can right-click on any location on the map and choose Rotate Here from the menu.
The rotor controller determines the direction the rotor must turn to move to the correct bearing. Click Long on the Map toolbar (or press Ctrl + F11) to rotate the antenna to the DX station's bearing using the long path. The Rotor menu on the Map toolbar also has buttons to turn the rotor in either direction. Stop the rotor at its current position by clicking Stop on the Map toolbar, or by pressing Alt + F11.
Antennas and associated rotors are configured in the File, Settings, Radio/Ant window. Each ham band has one preferred antenna assigned. If that antenna has a rotor, the rotor controls on the Map window are enabled and the radial direction lines are displayed. Antenna and rotor status are displayed in the status bar on the Map window. Up to 3 rotors can be assigned in CommCat, and each rotor can have more than one antenna.
As an antenna rotates, the radial lines on the map move to show its approximate position. The radial lines may dither slightly due to noise in the rotor position measuring circuitry. The rotor bearing must change by at least 1 degree before the bearing change is shown on the Great Circle Map. If the bearing change is less than 1 degrees, the radial lines may not move. Control whether or not rotor tracking is enabled using the Track Rotor option in the Rotor menu.
The bearing to the DX is found from the callbook you have specified. The bearing may be different from the bearing used to position the red line on the map since the spot bearing is found by an internal look up in CommCat based on the call's prefix. If a "/" (slash) is found in a call, it is assumed that station is portable. In this case the internal look up is used since the callbook data may not reflect the location of operation. You can turn off bearing lookup in File>Settings>Spots>DX Summit>Call Lookup if you are not using a rotor.
Gray line
The gray line shows the current dusk/dawn line. In other words, the gray line shows the transition between night and day on the map. Often times radio propagation is enhanced between two points along the gray line.
The night-to-day transition is shown in red, while the day-to-night transition is shown in black. The region in the world where it is night is shaded with gray diagonal lines.
The gray line is drawn when the map is centered on your "home" location. If you have shifted the center of the map to another location using the right mouse menu, the gray line is not drawn. The gray line is enabled on the File, Settings, Spots window.
As time passes, the position of the gray line changes to reflect the new relative position of the earth and sun. Use the Refresh button on the Map toolbar to update the gray line manually.
Detail maps
A number of high resolution detail maps are provided with the CommCat Gold version. (If you have not installed the maps on your system, this section does not apply.) To see a regional map for an area of interest, move the mouse pointer over the part of the world you want to see, click the right mouse button, and choose Detail Map.
Copying the Map to the Clipboard
Copy the map image to the clipboard by choosing Copy from the CommCat Edit menu. Once on the clipboard you can paste the map image into any document that can accept clipboard images, including a QSL card design or word document.
Right Mouse Menu
Additional map functions are accessible through the right mouse menu. The menu is shown below.
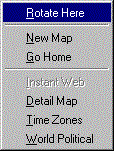
Rotate Here |
Rotate the present antenna to the mouse position |
New Map |
Redraw the map using the current mouse pointer position as center. |
Go Home |
Restore the map center to the longitude and latitude specified in File, Settings, Station, Station. |
Instant Web |
Create an Instant Web Page for the spot identified by the mouse pointer. (This menu option is disabled if the mouse pointer is not over a spot marker.) |
Detail Map |
Display a detailed map of the region identified by the mouse pointer position. |
Time Zones |
Display the world time zone map in a new window. |
World Political |
Display the world political map in a new window. |