Overview
The CommCat RTTY window provides a way to send and receive RTTY (Radio Teletype) signals. RTTY is one of the earliest digital modes, becoming popular when surplus Teletype machines were relatively easy to find. CommCat RTTY uses the sound card in your computer to send audio tones to you microphone input and receive tones from your radio audio. When tones are used to send RTTY, the technique is called AFSK (audio frequency shift keying). It is also possible to key the radio's VFO using FSK.
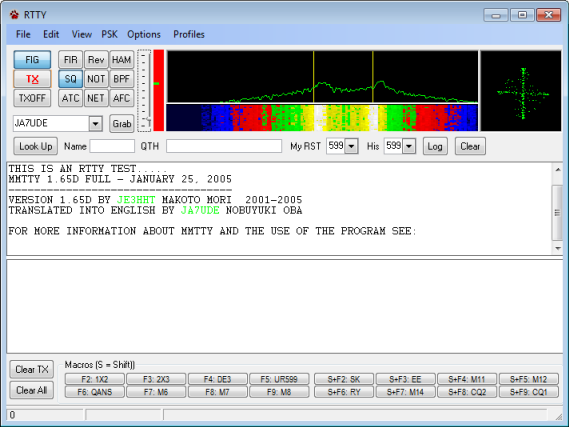
There are many web sites that provide great detail on the theory and operation of RTTY. A good place to start for an historical background is http://www.rtty.com.
An excellent getting started guide for MMTTY can be found here: http://www.aa5au.com/gettingstarted/rtty_downloadmmtty.htm. Here is a link to the MMTTY User Group on Yahoo: http://groups.yahoo.com/group/MMTTY/
MMTTY
CommCat uses the MMTTY engine by Makoto Mori, JE3HHT, and Dave, AA6YQ. MMTTY is a free standalone program that can be used to operate RTTY without CommCat. CommCat uses the program through an interface the author provided to allow other programs to provide RTTY as an internal function.
Download and install MMTTY using this link:
http://mmhamsoft.amateur-radio.ca/mmtty/index.html
Start MMTTY by double-clicking the MMTTY icon. By running the program you will confirm that the installation was correct.
Configuring CommCat for MMTTY
Once you have confirmed that MMTTY has been installed correctly, start CommCat and open the Station Settings window (File, Settings, Station). In the Station Settings window, click Modes, then RTTY Options.
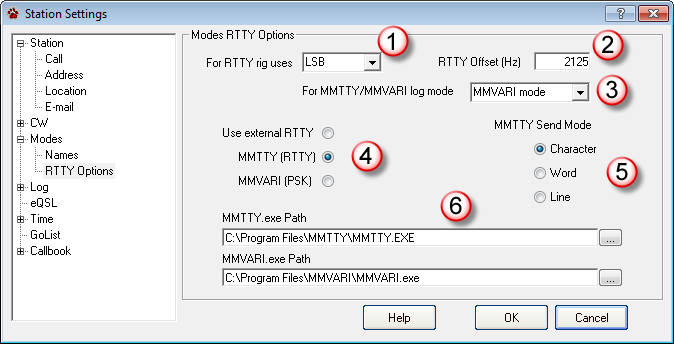
The following steps assume you will use AFSK to send RTTY.
1. Choose the mode your radio uses to send and receive AFSK in the For RTTY... list. The LSB single-sideband mode is traditionally used for AFSK, although USB is becoming more common..
2. The RTTY Offset determines the Mark frequency offset. Your radio VFO is the suppressed carrier frequency, while the Offset is the number of Hertz the suppressed carrier is from the Mark frequency. Enter a positive number for LSB and a negative number for USB. The common offsets are:
•2125
•2000
•1700
•1445
•1275
•1170
•1000
•915
3. Select the mode you wish to appear in your log when you log a contact when using MMTTY or MMVARI.
4.Select the MMTTY (RTTY) radio button. When the RTTY window is open, CommCat assumes the mode is your selected mode no matter what mode is reported by your radio. In addition, the RTTY Offset is applied when you log a station, and when tuning by double-clicking a spot. The frequency shown in the lower left corner of the CommCat main window is always the VFO frequency, not the offset (transmit) frequency.
5. Select the MMTTY Send Mode you wish to use. The Word and Line mode options hold the outgoing stream of data so you can make corrections if you make a typing mistake.
6. Enter the path to MMTTY.exe in the MMTTY Path box. If you installed MMTTY without making any changes, MMTTY is found in C:\Program Files\MMTTY\MMTTY.exe.
Additional settings are provided from the CommCat RTTY menu bar.
RTTY Options
Many options for the MMTTY engine can be accessed from the RTTY menu bar by clicking Options, Setup Engine. The Setup Engine options are explained in detail in MMTTY Help. Be sure to set the Mark and Ham Default frequencies to match your desired offset. The options are found in the Demodulator tab. For example, if you wish to use a 1445 Hz offset, select 1445 in the Discriminator Mark list, and enter 1445 in the first box for the HAM Default.
Set the font and background colors for the RTTY text windows in the Colors and Fonts... selection of the Options menu.
Select CommCat RTTY options... to open the CommCat Modes RTTY Options window.
The UOS (Unshift-On-Space) option cause the RTTY engine to go to the LTRS case each time a character space is encountered. UOS is useful to correct a stream of character that is stuck in FIGS case.
Use the View menu to customize the spectrum components that appear in the RTTY window. You may show or hide the waterfall or X-Y displays.
RTTY Window Layout
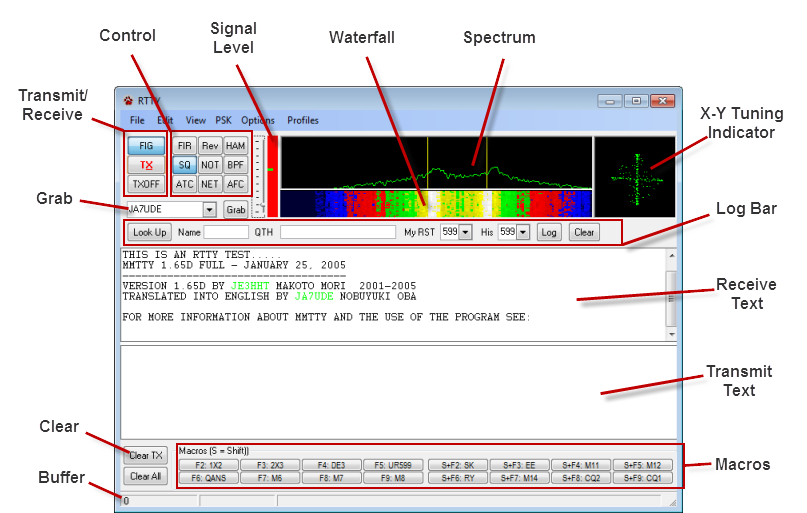
Transmit Receive |
|
FIG |
Indicates FIG or LTRS case or text in Receive Text window. Click to change case. |
TX |
Start Transmit mode. When in Transmit, click to end transmission when buffer is empty. |
TXOFF |
End transmission immediately. (You can also press ESC key.) |
Control |
|
IIR |
Type of Demodulator. Rotates between IIR, FIR, and PLL. |
Rev |
Toggles between regular and reverse shift. |
HAM |
Resets Marks and Shift values to their default values. |
SQ |
Enable squelch. Set the squelch level by clicking above or below the horizontal green tick mark on the Signal Level indicator. |
NOT |
Turns on the audio notch filter. The notch frequency is indicated by the small red arrow in the spectrum display. Change the notch frequency by right-clicking to the left or right side of the arrow. |
BPF |
Turn the band pass filter on and off. (It should normally be on.) |
ATC |
Turn the Automatic Threshold Control on and off. Turn off for low level signals. |
NET |
Sets the transmit mark frequency to the same frequency as the receive mark frequency. |
AFC |
Turn on and off Automatic Frequency Control. AFC locks the demodulator to a close-by signal. |
Signal Level |
|
Indicator |
Shows the incoming audio signal level. |
Level Slider |
Use the Level Slider to the left of the Signal Level Indicator to adjust the gain of the spectrum and waterfall displays. The slider does not affect the internal MMTTY engine characteristics. |
Threshold |
Shows the squelch level. Click above or below the green tick to set the level. |
Waterfall |
Displays incoming spectrum in a waterfall format. The mos recently received spectrum is at the top. The waterfall can be monochrome, or color. Click the View menu option to change the setting. |
Notch |
A red triangle shows the notch frequency |
Spectrum |
Displays the spectrum amplitude. |
X-Y Tuning Indicator |
Rotating X-Y display shows the Mark and Space tones. Mark is horizontal and Space is vertical. |
Log Bar |
|
Look Up |
Looks up name and QTH for current focus call. Set the focus call by clicking the Grab button after selecting a call in the Grab list, or by clicking a colored call in the Receive Text Window. |
Name |
Name of current focus call op. Obtained by clicking Look Up or by right-clicking a name in the Receive Text window. |
QTH |
QTH of the current focus call op. Obtained by clicking Look Up or by right-clicking a word in the Receive Text window. |
My RST |
RST report |
His |
RST report |
Log |
Log the current contact using the focus call, name, QTH and RST values. |
Clear |
Clears all log data entry boxes. |
Receive Text |
Displays the incoming text when in Receive, and the outgoing text when in Transmit. Use color settings to change the colors or incoming, transmitted, and call sign text. |
Transmit Text |
Displays the text to be sent, either from the keyboard, or by using a Macro. |
Macros |
CommCat has 16 macros you can program with canned messages. See the Macro help topic, below. |
Buffer |
Shows the number of characters remaining in the type ahead buffer. |
Clear |
|
Clear |
Clear the text in the Transmit (bottom) window |
Clear All |
Clears text in the Transmit and Receive (top) windows, the Name and QTH boxes, and the grab list. |
Grab |
As calls are found in incoming text in the Receive window, they are added to the Grab List. Click the Grab button to use the selected call as the DX Focus call. |
RTTY Macros
Sixteen macros are available in CommCat RTTY for inserting canned text into your transmitted text. Eight are accessed with function keys 2 through 9, and eight more by using the shift key. Special commands are available for use in the macros. For example, in the macro shown below, %c is replaced by the focus call and %m is replaced by your call. The resulting transmission would say "N6OJ de W6HN" if I (W6HN) were working N6OJ.
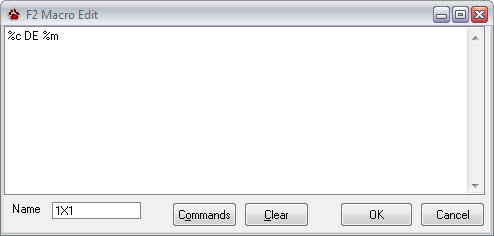
Open the Macro Edit window by right-clicking over the key you want to use. You can also open a Macro Edit window through the Edit option in the RTTY menu bar. Once the window is open, add or edit the contents of the macro in the text box. Name the macro in the name box. This name appears on the button as a caption. To see a list of commands available, click the Commands button.
Receive Text Right-Click Menu
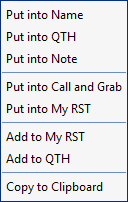
Right-click over text in the Receive Text panel to grab text and use it for special purposes.
Open MMTTY RTTY Window
Click PSK on the RTTY Menu bar to close the RTTY window and open the MMVARI BPSK window.
Call sign Coloring
The Colors and Fonts setting window provides a way to set the fonts, font colors, and background colors for the Receive and Transmit windows. Click a color to change it.
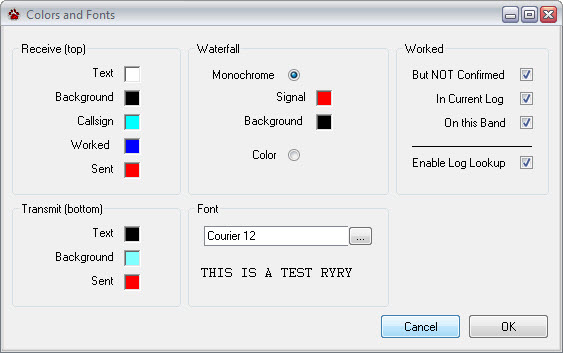
When CommCat identifies a call sign, it is painted the color you have chosen. You can also use the Worked filter to use an alternate color for a call sign you have worked previously. Select the options in the Worked group you wish to use. For example, the Worked color will be used for calls that have been worked but not confirmed, in the current log, and on the current band.
CommCat Mode Control
When you are using MMTTY to operate RTTY, the Lock mode button is activated. This means that the mode used for your radio and the mode used for logging are determined by the RTTY settings. If you change modes by using your radio control panel, the modes used by CommCat remain as set.
PTT
If you wish to use PTT to control your radio transmit/receive function, use the PTT settings in File>Settings>Radio/Ant>Radio x>PTT. The PTT setting in MMTTY Settings does not function in CommCat.