Overview
The CommCat PSK window provides a way to send and receive BPSK (Binary Phase-Shift Keying) signals. PSK is one of the most popular digital modes. Because of its narrow bandwidth, successful communications using low power are possible. CommCat PSK uses the sound card in your computer or an external sound device such as a SignaLink, to send audio tones to your transmitter and to receive tones from your receiver. The PSK window can also be used for the RTTY mode using AFSK. Note that RTTY AFSK is also possible using CommCat's MMTTY window.
MMVARI
MMVARI was written by Makoto Mori, JE3HHT. The PSK engine is experimental and is a Beta release. Mako has also released a standalone MMVARI program you should download from the link below. CommCat uses the setting file created by the standalone MMVARI program, so it is important to download and install before you use CommCat MMVARI.
Here are several links to additional information about PSK:
MMVARI Home Page |
|
Wikipedia article on phase-shift keying and its many variations: |
|
Wikipedia article on PSK31, the most popular ham mode for PSK: |
|
PSK introduced by Steve Ford, WB8IMY, at ARRL: |
|
How-to article for PSK31: |
Configuring CommCat for MMVARI
Start CommCat and open the Station Settings window (File, Settings, Station). In the Station Settings window, click Modes, then RTTY Options.
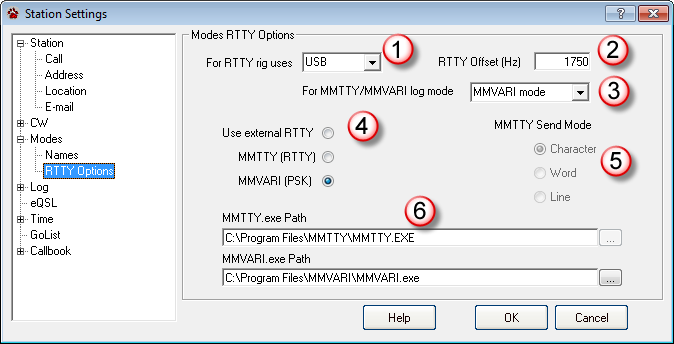
1 |
Select the Mode your radio uses to send/receive PSK (traditionally LSB, but many now use USB) |
2 |
The RTTY Offset is set in the PSK window when you click a signal. Ignore the setting here since the offset is determined by the MMVARI engine.. |
3 |
Select the mode you want to use in your log when you log a contact. |
4 |
Select the MMVARI engine. Note that when the PSK window is open, the log mode is determined by the mode selected in the RTTY Settings window (3). |
5 |
The MMTTY Send Mode is not used by the PSK window |
6 |
MMTTY path is not used by the PSK window. Enter the path to MMVARI.exe. This path is used to find the settings for MMVARI. |
MMVARI Settings
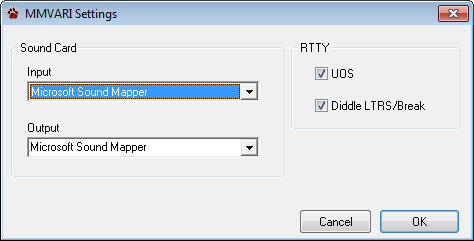
Select MMVARI Options from the View menu to open the Settings window.
Select the Input and Output sound devices to be used by MMVARI.
In the RTTY group, put a check in UOS to use Unshift-on-Space when receiving RTTY using MMVARI.
Put a check in Diddle LTRS/Break to use the Break code (instead of Letters) when you are receiving RTTY using MMVARI. It is not possible to turn off diddle when transmitting.
Additional MMVARI settings can be found through the MMVARI standalone program. Any settings made there are also used by the CommCat BPSK window.
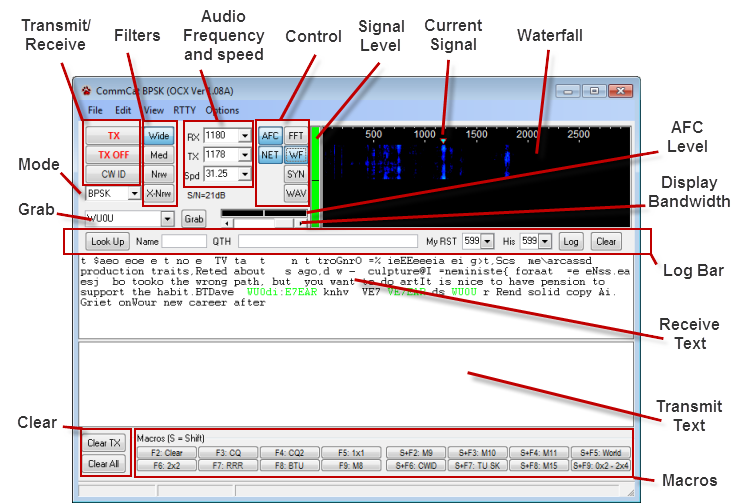
PSK Window Layout

Item |
Description |
|---|---|
Transmit/Receive |
Click TX to start a transmission. The TX button caption changes to RX. Click RX to end a transmission. Once the output buffer is empty, MMVARI goes back to receive.
Click TX OFF to end a transmission immediately without waiting for the output buffer to clear. The Escape (ESC) key can also be used to end a transmission immediately.
CW ID puts a CW identification at the end of a transmission. |
Filters |
Select Wide Med (Medium), Nrw (Narrow), or X-Nrw (Extra Narrow) audio input filters. |
Audio Frequency and Speed |
The audio frequency for Transmit, Receive, and the Baud rate are shown. You can set them from these boxes. The TX and RX frequencies are normally set by clicking a signal in the spectrum display. The audio frequencies are added to the VFO frequency to establish the operating frequency. |
Control |
AFC controls the Automatic Frequency Control function which tracks signals. NET locks the Transmit and Receive frequencies together. If you wish to operate split, click this button. Normally NET should be on.
FFT (Fast Fourier Transform) displays the amplitude-vs-frequency of the audio input.
SYN shows the envelope of the decoded signals.
WAV shows the waveform of the received signals
WF displays a waterfall of the input signal.
|
Signal Level |
Displays the signal level of the received signal |
Waterfall |
Displays the received signal as FFT, Waterfall, Sync, or Wave. Right-click over the display for additional options, including setting notch frequencies. |
Current Signal |
The triangle shows the current receive frequency. With NET set, the transmit and receive frequencies are the same. When NET is not set, the transmit frequency appears as an unfilled red triangle. |
AFC Level |
Displays current AFC activity |
Display Bandwidth |
Adjusts the bandwidth of the frequency display. |
Log Bar |
Click Log to add the QSO to your log using the parameters shown in the Log box. |
Receive Text |
Incoming text. Text that is being transmitted also appears in this panel in the color you have selected (see below). |
Transmit Text |
Outgoing text |
Macros |
16 programmable macros that can be used to send text. See below. |
Clear |
Clear the Transmit or both panels |
Grab |
Use the call shown in the combo box as the DX Focus call. |
Mode |
Set the mode for the PSK window. Selections include BPSK, RTTY and MFSK. This mode is used when contacts are logged (the radio mode is not logger). |
PSK/RTTY Macros
Sixteen macros are available in CommCat BPSK for inserting canned text into your transmitted text. Special commands are available for use in the macros. For example, in the macro shown below, %c is replaced by the DX Focus call and %m is replaced by your call. The resulting transmission would say "N6OJ de W6HN" if I (W6HN) were working N6OJ.
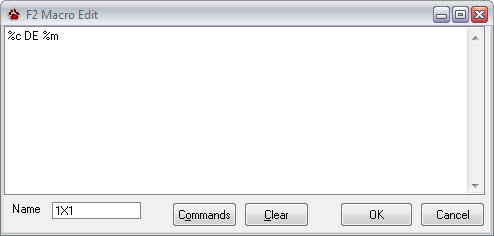
Open the Macro Edit window by right-clicking over the key you want to use. You can also open a Macro Edit window through the Edit option in the BPSK menu bar. Once the window is open, add or edit the contents of the macro in the text box. Name the macro in the name box. This name appears on the button as a caption. To see a list of commands available, click the Commands button.
Receive Text Right-Click Menu
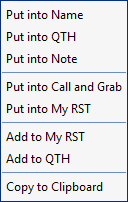
Right-click over text in the Receive Text panel to grab text and use it for special purposes.
Open MMTTY RTTY Window
Click RTTY on the BPSK Menu bar to close the BPSK window and open the MMTTY RTTY window.
Call sign Coloring
The Colors and Fonts setting window provides a way to set the fonts, font colors, and background colors for the Receive and Transmit windows. Click a color to change it.
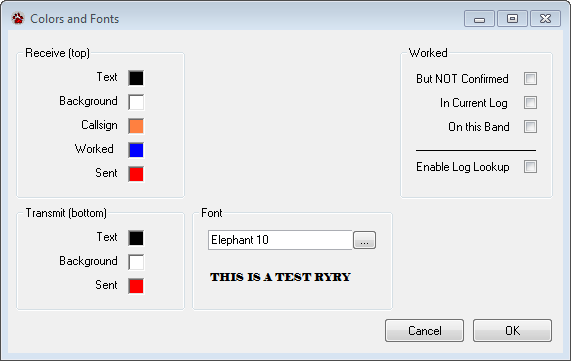
When CommCat identifies a call sign, it is painted the color you have chosen. You can also use the Worked filter to use an alternate color for a call sign you have worked previously. Select the options in the Worked group you wish to use. For example, the Worked color will be used for calls that have been worked but not confirmed, in the current log, and on the current band.
CommCat Mode Control
When you are using MMVARI to operate with a digital mode, the Lock button on the Main Mode Toolbar is activated. This means that the mode used for your radio and the mode used for logging are determined by the RTTY settings. If you change modes by using your radio control panel, the modes used by CommCat remain as set.
PTT
If you wish to use PTT to control your radio transmit/receive function, use the PTT settings in File>Settings>Radio/Ant>Radio x>PTT.